What Sugar Does Rna Have
The primary difference between sugar in Dna and RNA is that sugar in DNA is deoxyribose whereas saccharide in RNA is ribose.
Saccharide in DNA and RNA are two components of nucleic acids, Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA. Unremarkably, nucleic acids contain pentose sugar, which is cyclic.
Key Areas Covered
- What is Sugar in Deoxyribonucleic acid
- Definition, Characteristics, Importance
- What is Sugar in RNA
- Definition, Characteristics, Importance
- Similarities Between Sugar in DNA and RNA
- Outline of Common Features
- Difference Between Sugar in DNA and RNA
- Comparing of Key Differences
Key Terms
Sugar in Deoxyribonucleic acid, Sugar in RNA
What is Saccharide in Dna
Sugar in DNA is the deoxyribose component of the DNA nucleotide. DNA is a polymer of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a helical structure. The monomeric unit of the DNA polymer is the Deoxyribonucleic acid nucleotide. Generally, each Dna nucleotide is composed of a deoxyribose carbohydrate, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. In addition, the nitrogenous base and the phosphate grouping are attached to the deoxyribose carbohydrate. Therefore, deoxyribose is the blazon of sugar that occurs in DNA.
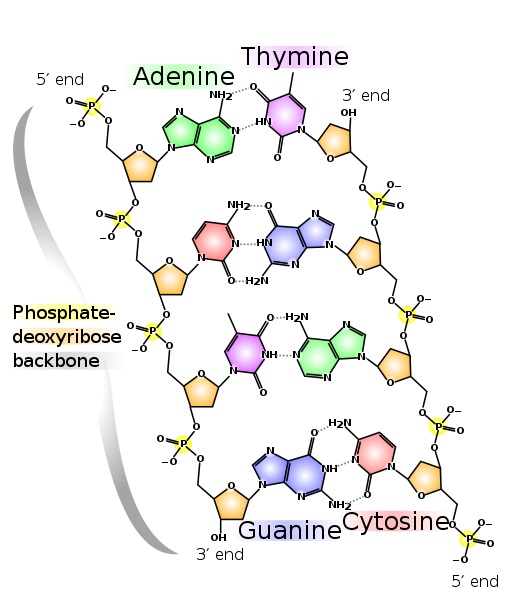
Figure 1: Saccharide-Phosphate Backbone in Dna
Furthermore, Dna is a double-stranded molecule that stores biological information. Dna undergoes replication to produce the aforementioned copy of the molecule during reproduction. Normally, the courage of the Deoxyribonucleic acid molecule is a sugar-phosphate backbone. Phosphodiester bonds are responsible for the polymerization of DNA nucleotides to form the polynucleotide chain. More than importantly, a phospho-diester bail is a covalent bail that occurs between sugar and a phosphate group of the 2 DNA nucleotides. This bail occurs betwixt the third and the fifth carbon atoms of the next Deoxyribonucleic acid nucleotides. 2-Deoxyribose is the pentose sugar that occurs in the polynucleotide concatenation of Deoxyribonucleic acid.
What is Sugar in RNA
Sugar in RNA is a ribose carbohydrate and this ribose saccharide is a five-carbon sugar molecule, a pentose. RNA is also a polymeric molecule with a carbohydrate-phosphate courage. Similarly, the phosphor-diester bonds occur between the third and the fifth carbon atoms of the adjacent RNA nucleotides. Nevertheless, RNA nucleotides are the monomeric units of the polymer, RNA. More often than not, RNA is a polymeric molecule with various biological roles in the coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. Unlike DNA, RNA occurs in single strands.
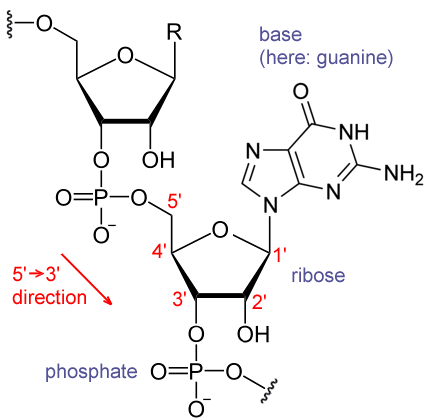
Figure 2: Sugar in RNA
Moreover, ribose is the sugar in RNA while in Deoxyribonucleic acid it is 2-deoxyribose. Therefore, the main difference betwixt the sugars in Dna and RNA is the presence of a hydroxyl group in the second carbon molecule of the pentose band structure. Besides, DNA is fabricated upwards of Dna nucleotides while RNA is made up of RNA nucleotides. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are the 4 nitrogenous bases that occur in DNA nucleotides. Notwithstanding, in RNA nucleotides, the four nitrogenous bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
Similarities Between Saccharide in Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA
- Sugar in DNA and RNA is the pentose sugar that occurs in the nucleotides.
- DNA and RNA are polynucleotide chains with a sugar-phosphate backbone.
- The phospho-diester bonds occur between the third and the 5th carbon atoms of the sugar.
Difference Betwixt Carbohydrate in Dna and RNA
Definition
Sugar in Deoxyribonucleic acid refers to the pentose carbohydrate molecule occurring in the carbohydrate-phosphate courage of DNA, which is deoxyribose, while sugar in RNA refers to the pentose sugar molecule occurring in the sugar-phosphate backbone of RNA, which is ribose.
Type of Pentose Sugar
2-deoxyribose is the blazon of sugar in DNA while ribose is the blazon of sugar in RNA.
Chemic Construction
ii-Deoxyribose lacks a hydroxyl group in the second carbon atom of the pentose ring, while ribose contains a hydroxyl group in the 2d carbon atom of the pentose ring.
Conclusion
In cursory, saccharide in DNA and RNA is the pentose sugar that occurs in the sugar-phosphate backbone of the polynucleotide chains of DNA and RNA. In full general, 2-deoxyribose is the sugar that occurs in the polynucleotide chain of Dna while it is ribose in RNA. 2-deoxyribose, which is the sugar in Deoxyribonucleic acid, lacks a hydroxyl group in the second carbon atom of the pentose ring. However, ribose, which is the carbohydrate in RNA, contains a hydroxyl group at the second carbon cantlet of the pentose ring. More importantly, Dna and RNA are polynucleotides that shop biological data, assuasive coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. However, the chief difference between sugar in DNA and RNA is the presence of a hydroxyl group at the second carbon of the pentose sugar in the sugar-phosphate backbone.
References:
- "RNA." Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 17 Sept. 2022.
- "Dna." Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 28 Aug. 2022.
Image Courtesy:
- "Dna chemical structure" By Madprime – Own work (CC Past-SA iii.0) via Commons Wikimedia
- "RNA chemical structure " Past en:User:Narayanese – Own Work (CC BY-SA iii.0) via Commons Wikimedia

What Sugar Does Rna Have,
Source: https://pediaa.com/what-is-the-difference-between-sugar-in-dna-and-rna/
Posted by: kingrepasustem.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Sugar Does Rna Have"
Post a Comment